Date Published: Jan. 10, 2025
The recent rise of Augmented Reality (AR) technologies is reshaping many industries, from entertainment and retail to healthcare and enterprise. One of the increasingly more demanding in this field is Near-to-eye Displays (NED), such as AR glasses or headsets, as they offer key advantages such as portability, immersive user experience, and even Hands-free interaction with digital contents.
For wide Field-of-View (FOV) AR glasses, high index glass and/or exotic materials such as SiC, or silicon carbide, are employed, that increase material costs of AR glasses.
The student research team from Prof. Yuzuru Takashima’s lab at the University of Arizona developed a solution to double or triple FOV. The paper “Expanding field-of-view of near-to-eye display by hybrid angular and wavelength multiplexing” demonstrated a Volume Holographic Grating (VHG) doubles the FOV of existing AR NED systems with minimum modification, and it enables to use a low cost and low index materials such as plastic and BK7 glasses.
Authors of the paper include, Pengyu Liu, Chuan Luo, Ted L. Lee, Gregory Nero, Tianyao Zhang, Yexin Pei, Xianyue Deng, and Yuzuru Takashima
This FOV expander concept is expected to provide a low-cost, easy to fabricate solution to AR-NED systems that require wide FOV, without needing to increase the index of refraction of the image guide material. This is an exciting step forward in the next stage of immersive technologies.
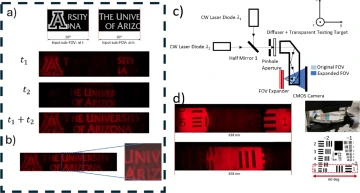
Use holographic FOV expander to project two transparent targets at different time with different wavelengths. (a) The transparent objects used to create two sub-FOVs at two time domains when using two different wavelength: FOV using subFOV1 at t1 with lambda = 638 nm; FOV using subFOV2 at t2 with lambda = 658 nm; and using Matlab to overlay the two FOVs to simulate what real time image looks like with time-multiplexing. (b) An enhanced view of effects from crosstalk between two wavelengths. (c) Use holographic FOV expander via a see-through geometrical waveguide. Dashline shows the curved half mirror as the output coupler embedded in the geometrical waveguide as a output coupler. (d) Results shown of a USAF test target through the geometrical waveguide.
